|
Punnett Squares
Punnett Squares Made Easy!
Download
"cheat sheet"
Below is a sampling of Punnett
Square problems that you will be expected to solve. In order to do this,
you will have to understand the meaning of the terms below.
Genotype: The
letters that make up the individual. E.g. TT or Tt
Phenotype: The
physical characteristics of the particular trait. E.g. Tall or short
Dominant trait: Signified
by capital letter-E.g. T.
If the traits you are using are dominant or
recessive, this trait will "overpower" the recessive trait and will be
expressed. E.g. Tt
Recessive trait: Signified
by small case letter-e.g. t. An organism with a recessive
allele for a particular form of a trait will have that form only when the
dominant allele for the trait is not present
Homozygous: Has
same letters. E.g. TT or tt (same
alleles for trait)
Heterozygous: Has
different letters. E.g. Tt (different alleles for
trait)
Purebred trait: Also
known as true breeding. Individuals
genotype is homozygous and will only make one type of gamete. E.g TT
will always produces T, and T. tt will always produce t, and
t.
Gamete: sex cells. Represented
by letter N (meaning they are haploid-contain half the chromosomes
P generation: The
parental generation (Usually the first one in a genetic cross)
F1 generation: The
first generation of offspring from P generation (means first
filial: Latin for "son")
F2 generation: The
second generation of offspring from P generation (means
first filial: Latin for "son")
Monohybrid Cross: Also
known as a Single-Factor Cross. Only one trait is used in the genetic
cross. E.g. T=Tall, t=short. Example: Tt x Tt
Dihybrid Cross: Also
known as a Two-factor Cross. Two trait are used in the genetic
cross. E.g. T=Tall, t=short & B=Black fur, b=white
fur. Example TtBb x TTBB
Incomplete Dominance: One
allele is not completely dominant over the other. There is a blending with
the heterozygous offspring. E.g. RR=Red, Rr=Pink, and rr=white
Co-dominance: Both
alleles contribute to the phenotype. Offspring will have combination of
two alleles. E.g. RR=Red hair, Rr=Roan (mix of red and white hairs-almost
looks pink), and rr=white
Sex-linked trait: Genes
located on the sex-chromosomes called sex-linked genes.
Usually found on the X chromosome. X-linked alleles are
always expressed in males because males have only one X chromosome.
Multiple Alleles: There
are more than two-choices for the allele. Example is human blood group
genes. There are three possible alleles for this gene. IA,
IB, and i. IA and IB
are co-dominant. There are four possible phenotypes: A,
B, AB, and O.
Genotypic ratios: The
ratio of different genotype in the offspring from a genetic cross. E.g
1:2:1
Phenotypic ratios: The
ratio of different phenotypes in the offspring from a genetic cross. E.g 3:1
Sample Problems
|
Monohybrid
(Dominant and Recessive)
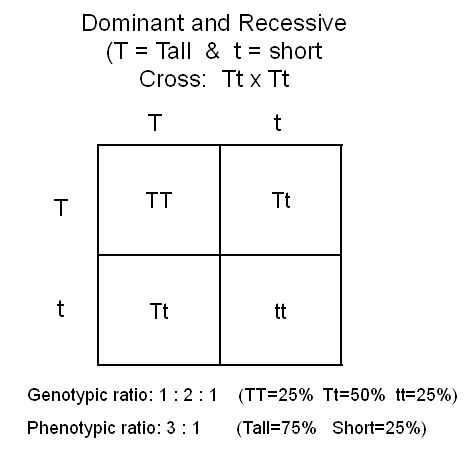
PROBLEM:
Cross two heterozygous Tall pea plants. Give genotypic and
phenotypic ratios.
STEP
1: Determine what kind of problem you are trying to
solve.
-
Does
it involve simple dominant and recessive traits, Incomplete
dominance, or Co-dominance?
-
Is
it a monohybrid or dihyrid?
-
In
this case there is only one trait..........this is a monohybrid
cross involving dominant and recessive traits.
STEP
2: Determine letters you will use to specify traits.
STEP
3: Determine parents genotypes.
STEP
4: Make your punnet square and make gametes (these go on the top
and side of your punnett square.
STEP
5: Complete cross and determine possible offspring.
STEP
6: Determine genotypic and phenotypic ratios.
-
Genotypic
ratio: Make a list of all the different genotypes (the
letter combinations) and determine how many of each you have.
-
Phenotypic
ratio: Make a list of all the different phenotypes (physical
characteristics.
|
 |
|
Monohybrid
(Incomplete Dominance)
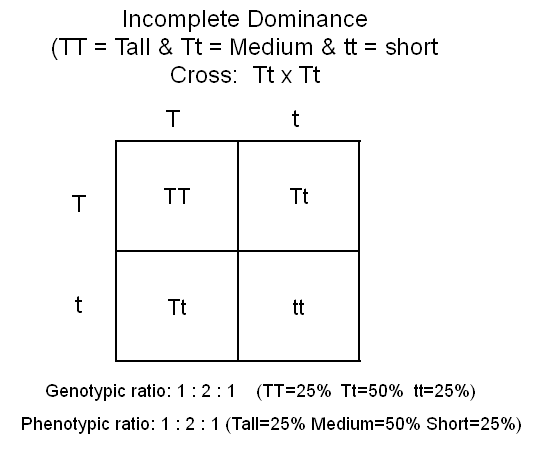
PROBLEM:
Cross two heterozygous plants. Give genotypic and phenotypic
ratios. The tall gene is this plant is incompletely dominant over
the short gene. TT=Tall, Tt=medium, and tt=short.
STEP
1: Determine what kind of problem you are trying to
solve.
-
Does
it involve simple dominant and recessive traits, Incomplete
dominance, or Co-dominance?
-
Is
it a monohybrid or dihyrid?
-
In
this case there is only one trait..........this is a monohybrid
cross involving incomplete dominant traits.
STEP
2: Determine letters you will use to specify traits.
STEP
3: Determine parents genotypes.
STEP
4: Make your punnet square and make gametes (these go on the top
and side of your punnett square.
STEP
5: Complete cross and determine possible offspring.
STEP
6: Determine genotypic and phenotypic ratios.
-
Genotypic
ratio: Make a list of all the different genotypes (the
letter combinations) and determine how many of each you have.
-
Phenotypic
ratio: Make a list of all the different phenotypes (physical
characteristics.
|
 |
|
Monohybrid
(Co-dominant)
PROBLEM:
Cross two heterozygous tan cows. Give genotypic and phenotypic
ratios. BB=Black, BW=tan, and WW=white
STEP
1: Determine what kind of problem you are trying to
solve.
-
Does
it involve simple dominant and recessive traits, Incomplete
dominance, or Co-dominance?
-
Is
it a monohybrid or dihyrid?
-
In
this case there is only one trait..........this is a monohybrid
cross involving co-dominant traits.
STEP
2: Determine letters you will use to specify traits.
STEP
3: Determine parents genotypes.
STEP
4: Make your punnet square and make gametes (these go on the top
and side of your punnett square.
STEP
5: Complete cross and determine possible offspring.
STEP
6: Determine genotypic and phenotypic ratios.
-
Genotypic
ratio: Make a list of all the different genotypes (the
letter combinations) and determine how many of each you have.
-
Phenotypic
ratio: Make a list of all the different phenotypes (physical
characteristics.
|
 |
|
Monohybrid
(sex-linked)
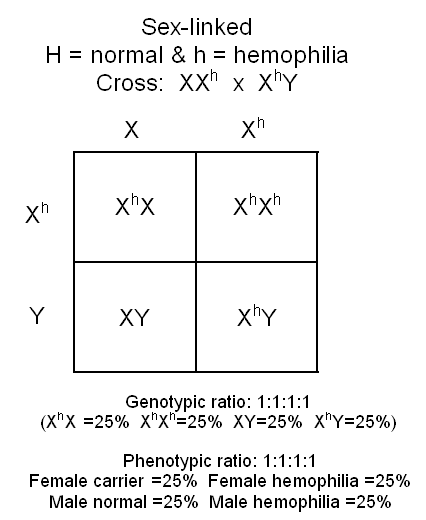
PROBLEM:
Cross a female carrier for hemophilia with a male with hemophilia.
H=normal, and h=hemophilia
STEP
1: Determine what kind of problem you are trying to
solve.
-
Does
it involve simple dominant and recessive traits, Incomplete
dominance, or Co-dominance?
-
Is
it a monohybrid or dihyrid?
-
In
this case there is only one trait..........this is a monohybrid
cross involving sex linked traits.
STEP
2: Determine letters you will use to specify traits.
-
In
this case it is a sex-linked problem. Remember that XX
is female, and XY is male. H=normal and
h=hemophilia. Normally you would not write the capital letters
on the genotypes, only the small case (the recessive gene responsible
for the disorder)
STEP
3: Determine parents genotypes.
STEP
4: Make your punnet square and make gametes (these go on the top
and side of your punnett square.
-
XhX
would make a Xh and X
-
XhY
would make a Xh and Y
-
NOTE:
The females gametes always go on top of the punnett square and the
males on the side.
STEP
5: Complete cross and determine possible offspring.
STEP
6: Determine genotypic and phenotypic ratios.
-
Genotypic
ratio: Make a list of all the different genotypes (the
letter combinations) and determine how many of each you have.
-
In
your problem this would be: XhX =
1, XhXh =
1, and XY= 1, and XhY
= 1 The genotypic ratio would therefore be 1 : 1 : 1
: 1
-
Phenotypic
ratio: Make a list of all the different phenotypes (physical
characteristics.
-
In
you problem this would be: Female Carrier = 1, Female w/
hemophilia = 1, Normal male = 1, and Male w/ hemophilia =
1.
The
phenotypic ratio would be 1 : 1 : 1 : 1
|
 |
|
Monohybrid
(Multiple Alleles)
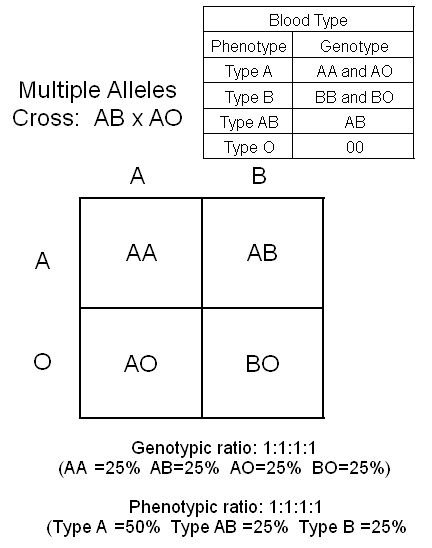
PROBLEM:
Cross a person with type AB blood with a person who is heterozygous for
type A blood.
STEP
1: Determine what kind of problem you are trying to
solve.
-
Does
it involve simple dominant and recessive traits, Incomplete
dominance, or Co-dominance, or multiple alleles?
-
Is
it a monohybrid or dihyrid?
-
In
this case there is only one trait..........this is a monohybrid
cross involving multiple alleles
STEP
2: Determine letters you will use to specify traits.
-
There
are more than two-choices for the allele. Example is human blood
group genes. There are three possible alleles for this
gene. IA, IB, and i. IA
and IB are co-dominant.
There are four possible phenotypes: A, B, AB, and O.
STEP
3: Determine parents genotypes.
STEP
4: Make your punnet square and make gametes (these go on the top
and side of your punnett square.
STEP
5: Complete cross and determine possible offspring.
STEP
6: Determine genotypic and phenotypic ratios.
-
Genotypic
ratio: Make a list of all the different genotypes (the
letter combinations) and determine how many of each you have.
-
In
your problem this would be: IAIA
= 1, IAIB=
1, and IAi
= 1, and IBi
= 1 The genotypic
ratio would therefore be 1 : 1 : 1 : 1
-
Phenotypic
ratio: Make a list of all the different phenotypes (physical
characteristics.
-
In
you problem this would be: Type A = 2, Type AB = 1,
and Type B = 1
-
Therefore
the phenotypic ratio is: 2 : 1 : 1
|
 |
|
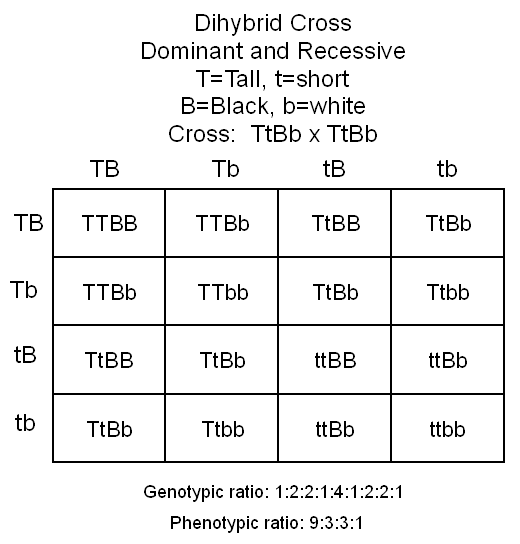
Dihybrid
(Dominant and Recessive)
PROBLEM:
Cross two heterozygous Tall Black cows. Tall is dominant over short,
and Black is dominant over white. Give genotypic and phenotypic
ratios of offspring.
STEP
1: Determine what kind of problem you are trying to
solve.
-
Does
it involve simple dominant and recessive traits, Incomplete
dominance, or Co-dominance?
-
Is
it a monohybrid or dihyrid?
-
In
this case there are two traits.........this is a dihybrid cross
involving dominant and recessive traits.
STEP
2: Determine letters you will use to specify traits.
-
In
this case there are two traits you will need letters for. Use T
= Tall, and t = short for one trait, and B = Black, and
b = white for the second trait. These are both
dominant/recessive genes
STEP
3: Determine parents genotypes.
STEP
4: Make your punnet square and make gametes (these go on the top
and side of your punnett square.
-
Making
gametes for a dihybrid cross requires you use FOIL
(first-outside-inside-last)
-
TtBb
would make four different gametes = TB, Tb, tB, tb
STEP
5: Complete cross and determine possible offspring.
STEP
6: Determine genotypic and phenotypic ratios.
-
Genotypic
ratio: Make a list of all the different genotypes (the
letter combinations) and determine how many of each you have.
-
Phenotypic
ratio: Make a list of all the different phenotypes (physical
characteristics.
-
In
you problem this would be: Tall/Black = 9, and
Tall/white = 3, short/Black = 3, and short/white = 1.
-
The
phenotypic ratio would therefore be 9:3:3:1
|
 |
|
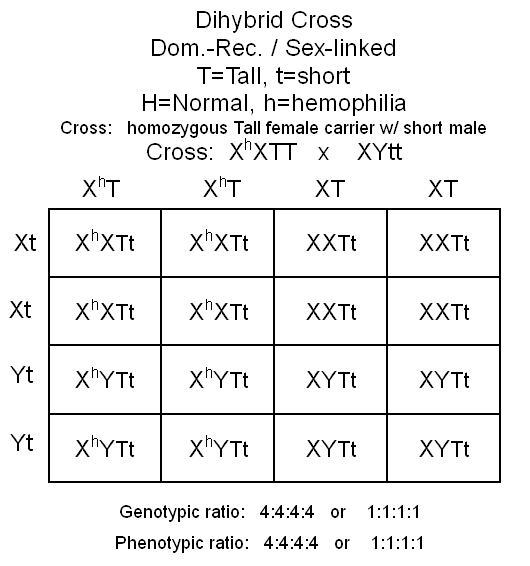
Dihybrid
(Dominant and Recessive and Sex-linked)
PROBLEM:
Cross a homozygous Tall female carrier for hemophilia with a short
normal male. Give genotypic and phenotypic ratios of offspring.
STEP
1: Determine what kind of problem you are trying to
solve.
-
Does
it involve simple dominant and recessive traits, Incomplete
dominance, or Co-dominance, or sex-linked?
-
Is
it a monohybrid or dihyrid?
-
In
this case there are two traits.........this is a dihybrid cross
involving dominant and recessive traits and sex-linked trait for
hemophilia.
STEP
2: Determine letters you will use to specify traits.
-
In
this case there are two traits you will need letters for. Use T
= Tall, and t = short for one trait, and H =normal, and
h = hemophilia for the second sex-linked trait. These
are both dominant/recessive genes
STEP
3: Determine parents genotypes.
STEP
4: Make your punnet square and make gametes (these go on the top
and side of your punnett square.
-
Making
gametes for a dihybrid cross requires you use FOIL
(first-outside-inside-last)
-
XhXTT
would make four different gametes = XhT,
XhT, XT, and XT
-
XYtt
would make four different gametes = Xt, Xt, Yt,
and Yt
STEP
5: Complete cross and determine possible offspring. When
you have a sex-linked trait, make sure you put the females gametes on top
of the punnett square and the male's on the side.
STEP
6: Determine genotypic and phenotypic ratios.
-
Genotypic
ratio: Make a list of all the different genotypes (the
letter combinations) and determine how many of each you have.
-
Phenotypic
ratio: Make a list of all the different phenotypes (physical
characteristics.
-
In
you problem this would be: Tall/female carrier = 4,
Tall/normal female = 4, Tall/male w/ hemophilia = 4, and
Tall/normal male = 4.
-
The
phenotypic ratio would therefore be 4:4:4:4 or 1:1:1:1
|
 |
|